How to Write the Domain of a Rational Function
The first is any natural domain restrictions due to the functions in the numerator and denominator themselves. Solve to find the x -values that cause the denominator to equal zero.
Inverse Domain And Range Of A Rational Function College Algebra Youtube
In any fraction if the denominator is zero then it is undefined.
. That is Domain R - a Find the domain of the rational function. Recall that the domain of a function is the se. The domain will then be all other x -values.
However the range of a rational function is not as easy to find as the domain. Y 1x. Since the equation is a quadratic we can solve it using the quadratic.
First determine the domain restrictions for the following functions then graph each one to check whether your domain agrees with the graph. When and when. Division by zero is undefined.
In this function we can see that there are two points for which it is not defined. The Domain of a Rational Function. Up to 10 cash back To find the excluded value in the domain of the function equate the denominator to zero and solve for x.
The denominator of a function is the bottom number or equation of a fraction. X2 2 x 15 0. Since each of these functions is a polynomial we dont have any restrictions from this part.
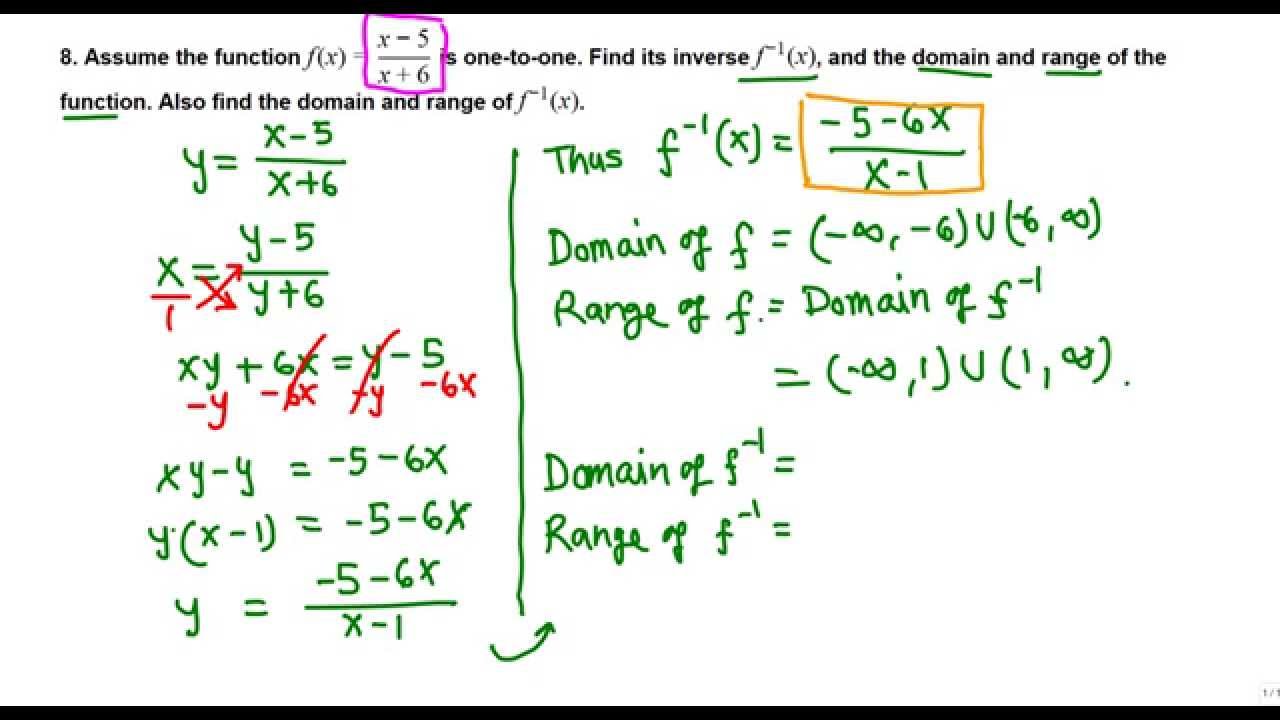
Let us consider the rational function given below. The range of the function is same as the domain of the inverse function. We set the denominator not equal to zero.
Therefore the domain of the rational function f x is all real values except x a. Having a zero as the denominator is equivalent to division by zero thus is also undefined. Domain of a Rational Function.
F x x x2 4. Set the denominator 0 and solve it for x. Determine the factors of the numerator.
You will have to know the graph of the function to find its range. X2 4 0. The rational function is undefined for any value of the variable that gives a zero denominator.
To find the domain Ill solve for the zeroes of the denominator. Set the denominator equal to zero. To find the domain of a rational function y fx.
Examine the behavior of the graph at the x-intercepts to determine the zeroes and their multiplicities. Find the domain and range of the rational function Largey x3 over x - 2 The domain of this function is exactly the same as in Example 7. For a simple example consider the rational function y 1 x y 1 x.
X2 4 x 2x 2 0 x 2. This means that the function is undefined when and. Set of all real numbers other than the values of x mentioned in the last step is the domain.
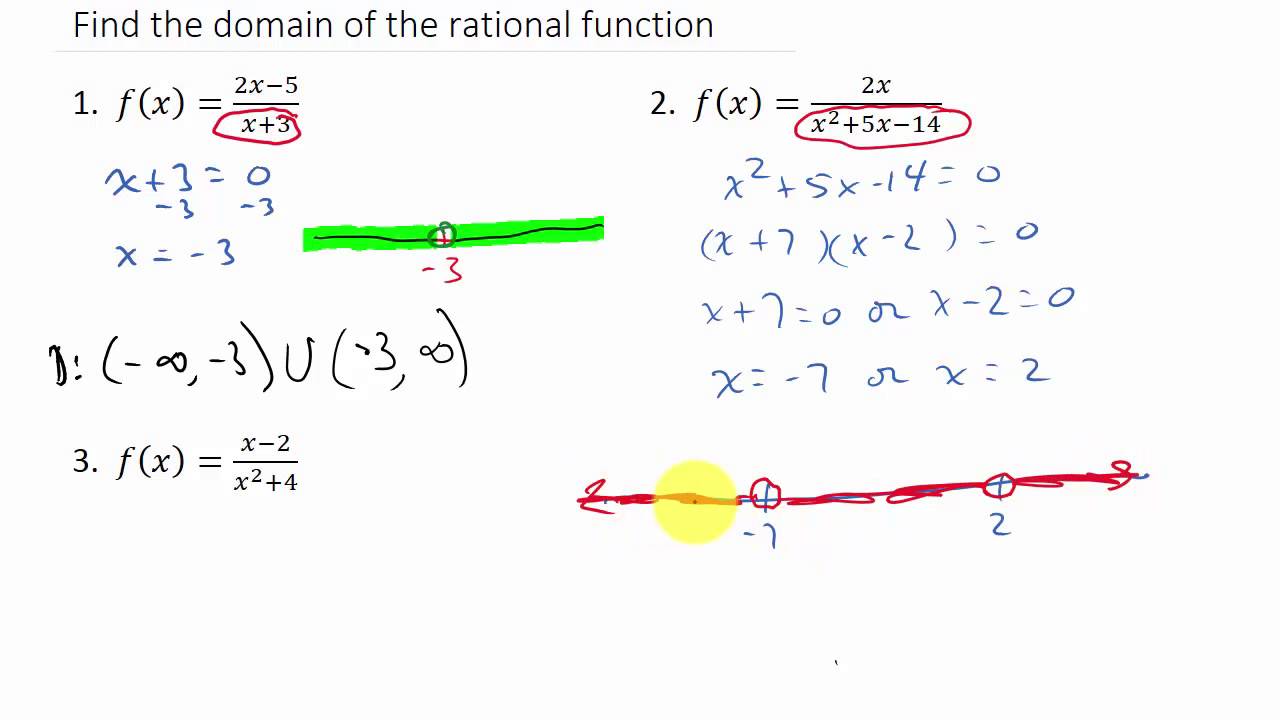
In order to find the domain of this rational function we need to check two types of domain restrictions. The domain of a rational function is all real numbers that make the denominator nonzero which is fairly easy to find. Therefore the domain of the function is all real numbers except -4 and 3 denoted.
Learn how to find the domain of rational functions with radicals in both the numerator and the denominator. By factoring the quadratic I found the zeroes of the denominator. We know that rational functions are only defined when their denominator is different from zero.
This is easy to do when finding the simplest function with small multiplicitiessuch as 1 or 3but may be difficult for larger multiplicitiessuch as 5 or 7 for. Learn how to find the domain of rational functions. - A rational function is a function of the form eqfx fracgxhx eq - A domain of a rational function is the set of values which independent variable x.
X 3 0 x 3 So the domain of the function is set of real numbers except 3. In this case the denominator is. X 5 x 3.
The domain is all real numbers except those found in Step 2. Domain is all real values of x for which y is defined. Let y fx be a function.
Given a graph of a rational function write the function. If there is any value of x for which y is undefined we have to exclude that particular value from the set of domain. Given a rational function find the domain.
Find the domain of fx 2x 1 3x - 2. Obviously that value is x 2 and so the domain is all x values except x 2. Find these values by creating an equation to solve.
X 5 x 3 0. Determine the factors of the numerator. Examine the behavior of the graph at the x-intercepts to determine the zeroes and their multiplicities.
The domain is comprised of all values of x 0 x 0. Determine the domain of the function. Equate the denominator to zero.
R x 3x5 x4 - 6x3 - 2 x2 - 9 Solution. Find the domain of the following expression. The domain of a rational function f x P x Qx f x P x Q x is the set of all values of x x for which the denominator Qx Q x is not zero.
When you are defining the domain of a function it can help to graph it especially when you have a rational or a function with an even root. Find the domain of the function. Given a graph of a rational function write the function.
Recall that the domain of a function is the set of possible input values x-values of the function. Solve the equation generated in Step 1. This is easy to do when finding the simplest function with small multiplicitiessuch as 1 or 3but may be difficult for larger multiplicitiessuch as 5 or 7 for.
The idea again is to exclude the values of x that can make the denominator zero. Find the Domain of a Rational Function.

How To Find Domain And Range Of Rational Functions 5 Mhf4u Youtube

How To Find The Domain Of A Rational Function In Interval Notation Study Com

No comments for "How to Write the Domain of a Rational Function"
Post a Comment